In any company there are plenty of both typical and custom processes, that concern production, finance, client interaction — that is, all the internal and external operations your company's success depends on.
As a rule, automation of business processes is the prerogative of big companies, whereas small businesses usually prioritize profitability and solid position on the market over everything else. However, it is exactly a small company that can adjust and run automated business processes quickly and smoothly. The greatest advantage of automation is having all company operations monitored and controlled at any stages from the very beginning, which also makes company growth a much easier experience than expected.
There is no universal business process scenario — each company has to introduce business algorithms of its own, that satisfy its specific requirements.
types of business processes
Basic — the ones concerning product creation, production, advertising, logistics, and sales. These business processes influence product price and its consumer value and provide for the company basic income. For example, Anna owns a small tailoring studio. The basic business process chain in her company starts with client's request → then goes selection of fabrics and design → after that, measurement → then the dressmaking itself → and, finally, the product is ready. The successfulness of result is measured by customer satisfaction.
Complementary — company's internal processes concerning finance, accounting, staff management, and control. These processes add up to the final product price, but have no consumer value. For instance, a client of a real estate agency has little interest in its staff issues.
Administrative — business processes involving management, planning, regulation, and control: for example, hiring and training of staff, or strategic solutions for company development and sustained competitive ability.
how to recognize a genuine business process
A genuine business process must be:
- Integral: that is, problem-solving and containing the actions to be performed in order to reach the desired effect.
- Described comprehensively and easy to understand.
- Considering all stages and participants of the process.
A business process is inefficient when:
- It has weak points. Some of the stages might hinder the smooth running of the whole process because of a tiny mistake, human factor, malfunctioning hardware or software, that may, for instance, cause processing of only a part of clients requests and, as a result, disrupt the deadlines for calls and sending commercial offers or price lists.
- It contains duplicate stages or actions, such as reoccuring submission documents for approval.
- It is not transparent and makes it difficult to monitor and assess its stage shifts and staff activity.
- It has problems with integration, such as incompatibility with existing software, which can cause glitches of all sorts and communication issues.
- It is unprofitable (even if it is non-profit). The successfulness of a business process can be monitored and measured by its key indicators, or by reaching the desired outcome.
why should you need automated business processes?

Imagine a situation, when:
- An employee broke his leg and can only be back to work in a month. His functions were temporarily delegated to another employee, who appeared to have his own style of doing the same tasks, that is taking much more time.
- Staff members have little idea of what they are doing and why. They have a vague understanding of their functions and duties.
- Managers see a lot of overall staff activity without knowing exactly who is doing what.
- Every new employee has to be instructed verbally, and from scratch.
- Staff instructions are inefficient or superficial.
- Employees are constantly shifting their responsibilities. There is no conformity and consistency among branches/departments.
- Staff is expanding without invoking better company performance.
- There is a perpetual mess in company documents, and a confusion of their versions: they are getting lost or impossible to track.
- Similar tasks are getting done much faster by competitors.
In order to avoid all sorts of office chaos, any company needs automated business processes. They have plenty of advantages:
- Employees have a clear idea of their functions, deadlines, and personal responsibility. It takes no time to get new staff members involved.
- Successfulness and efficiency become easy to monitor and assess.
- Weak points, such as time-consuming approval of documents, losses of client orders, and lack of conformity among employees and departments, become evident.
- Perspective thinking and strategic planning become possible.
how to create business processes
There are no universal or ideal business processes: each company has its own specific procedures that need to be simplified, improved, or corrected. Business processes vary, but the automation algorithm is always the same:
- Select business process participants: collect and analyze data in order to understand the role and functions of each employee in the process.
- Give the business process a name, and set its target.
- Define the starting and the ending points of the process.
- Define all the intermediate stages of the process.
- Select the executives for each stage and the whole process supervisor. Describe their functions.
- Set deadlines and estimate results.
- Describe all the points above in a flowchart or any other comprehensive format.
- Create this business process in the CRM.
- Brief the staff about it.
how to create business processes in apro crM
Whether you are managing a small company with just a few employees, or a huge conglomerate with dozens of departments and branches and even in-house production, storage and logistics, — you must be well-informed about all company processes and be able to monitor their efficiency at any time. Traditional workflow makes it difficult to do it, for the information in it has to undergo countless transformations in reports, discussions, and approvals. But if you are using CRM, you can easily replace standard business processes with automated ones — and start monitoring them regularly in the system. Clear and automated business processes make company workflow transparent at any stage and allow drawing conclusions about its efficiency and the necessity of changes.
In APRO CRM you can create automated business processes of any logic involving contacts, objects, activities, campaigns, and any other CRM elements. To create a business process, go to Main menu — Business processes (available to CRM administrators only):
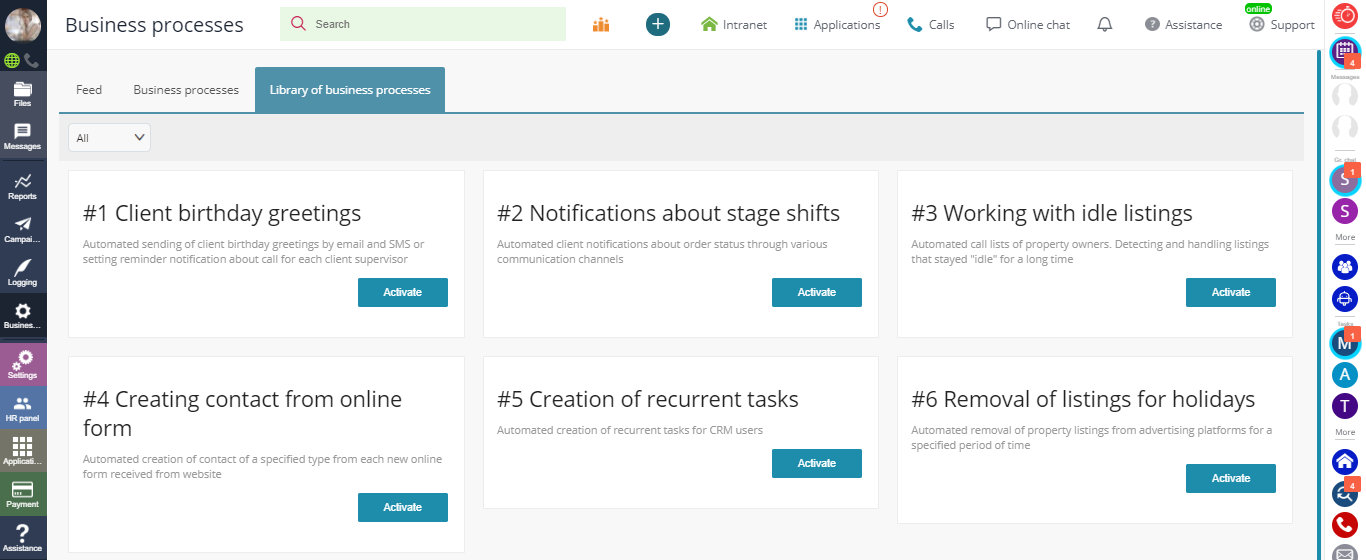
Here you can find a few ready-made samples stored in the Library of business processes:
Feel free to contact our support team for advice at any time.
nota bene
- Every company has business processes, but very few of them are monitored or automated.
- There is no universal business process template: each company has its own specific demands.
- In order to make your business processes work efficiently, they must be well analyzed, thoroughly described (including supervisors and executives), and automated in the CRM.
